Mudanças entre as edições de "CEL18702 AULA09"
Ir para navegação
Ir para pesquisar
| (15 revisões intermediárias pelo mesmo usuário não estão sendo mostradas) | |||
| Linha 3: | Linha 3: | ||
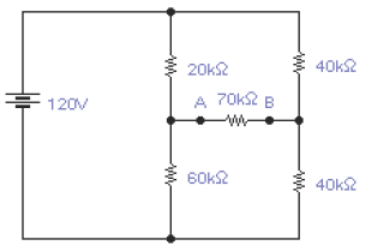
[1] Calcule o circuito equivalente utilizando o teorema de Thevenin | [1] Calcule o circuito equivalente utilizando o teorema de Thevenin | ||
| − | - Determine a tensão e a corrente na resistência de carga de 70k<math>\Omega</math> | + | - Determine a tensão e a corrente na resistência de carga de 70k<math>\Omega</math>. |
[[Imagem:fig40_CEL18702.png|center]] | [[Imagem:fig40_CEL18702.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Lembre-se: Você deve fazer os cálculos sem o o resistor de 70k<math>\Omega</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ;Resultado: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse top|Solução}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_{Th}=30V\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{Th}=35k\Omega\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_{N}=0,854mA\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Cálculo da resistência de Thevenin: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{Th}=(20.10^3//60.10^3)+(40.10^3//40.10^3)=35 k\Omega\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Cálculo da tensão de Thevenin <math>V_{Th}=V_{AB}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_{Th}=V_{AB}=V_{40k}-V_{20k}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_{Th}=\frac{120.40.10^3}{40.10^3+40.10^3}-\frac{120.20.10^3}{20.10^3+60.10^3}=30V\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cálculo da resistência de Norton: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_N=R_{Th}==35k\Omega\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cálculo da corrente de curto-circuito: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_N=I_{20k}-I_{60k}\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{eq1}=(20.10^3//40.10^3)= 13,3k\Omega\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{eq2}=(60.10^3//40.10^3)= 24k\Omega\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_1=\frac{120.24.10^3}{24.10^3+13,3.10^3}=77,2V\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_{20k}=\frac{120-77,2}{20.10^3}= 2,14mA\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_{60k}=\frac{77,2}{60.10^3}= 1,29mA\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_N=2,14.10^{-3}-1,29.10^{-3}=0,854mA\,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{collapse bottom}} | ||
| + | |||
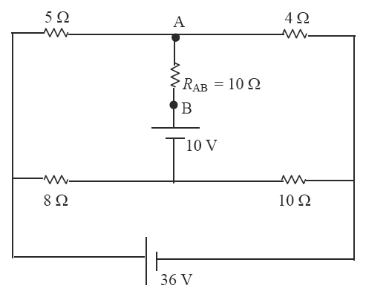
| + | [2] Determinar a corrente no resistor <math>R_{AB}</math> utilizando o teorema de Thevenin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Imagem:fig41_CEL18702.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Lembre-se: Você deve fazer os cálculos sem o o resistor de 10<math>\Omega</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
;Resultado: | ;Resultado: | ||
| Linha 11: | Linha 72: | ||
{{collapse top|Solução}} | {{collapse top|Solução}} | ||
| − | + | <math>V_{Th}=-14V\,</math> | |
| + | <math>R_{Th}=6,6\Omega\,</math> | ||
{{collapse bottom}} | {{collapse bottom}} | ||
| Linha 24: | Linha 86: | ||
! style="background: #ffd700;" | [[CEL18702_AULA08 | << ]] | ! style="background: #ffd700;" | [[CEL18702_AULA08 | << ]] | ||
! style="background: #faebd7;" | [[CEL18702 | <> ]] | ! style="background: #faebd7;" | [[CEL18702 | <> ]] | ||
| − | ! style="background: #ffd700;" | [[ | + | ! style="background: #ffd700;" | [[CEL18702_AULA10 | >> ]] |
|} | |} | ||
Edição atual tal como às 18h59min de 4 de março de 2016
Lista de Exercício 2
[1] Calcule o circuito equivalente utilizando o teorema de Thevenin
- Determine a tensão e a corrente na resistência de carga de 70k.
- Lembre-se: Você deve fazer os cálculos sem o o resistor de 70k.
- Resultado
| Solução |
|---|
|
Cálculo da resistência de Norton:
Cálculo da corrente de curto-circuito:
|
[2] Determinar a corrente no resistor utilizando o teorema de Thevenin.
- Lembre-se: Você deve fazer os cálculos sem o o resistor de 10.
- Resultado
| Solução |
|---|
|
|
Referências
[1] http://www.feng.pucrs.br/~virgilio/Circuitos_Eletricos_I/Capitulo3_ckt1.pdf
| << | <> | >> |
|---|